All You Need To Know About Breast Cancer
Overview
Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts. Breast cancer can occur both men and women, but it’s far more common in women. In fact, Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women and the second leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer.

However, breast cancer survival rates have increased, and the number of deaths associated with this disease is steadily declining, largely due to factors such as:
- Earlier detection
- New personalized approach to treatment
- A better understanding of the disease
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of breast cancer may include:
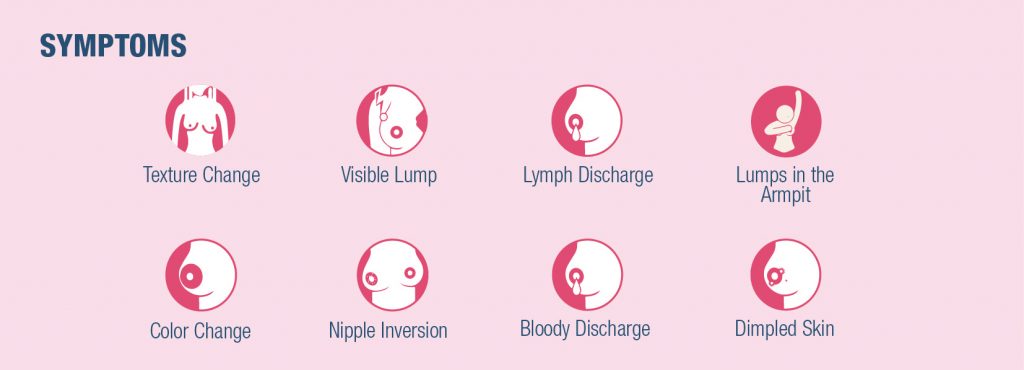
- A breast lump or tissue thickening
- Change in the size, shape or appearance of a breast
- Changes to the skin over the breast, such as dimpling
- Pigmented, peeling, scaling or flaking skin in the area around the nipple
- A newly inverted nipple
- Pain in the armpits or breast
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk
- A lump or swelling under the arm
Causes
Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast tissue mutate and divide rapidly. This excessive cell growth causes cancer because the tumor uses nutrients and energy and deprives the cells around it.
Typically, the breast cancer forms in either the lobules or the ducts of the breast. Lobules are the glands that produce milk, and ducts are the pathways that bring the milk from the glands to the nipple. Cancer can also occur in the fatty tissue or the fibrous connective tissue within the breast.
Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
What are the Risk Factors for Breast Cancer?
Factors that are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer include:
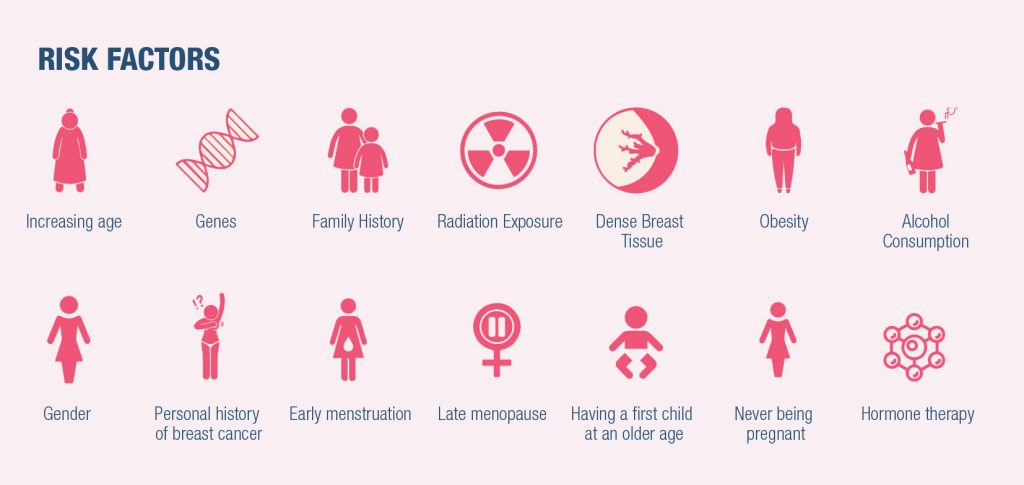
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop breast cancer.
- Increasing age: Risk for developing breast cancer increases with age. Most invasive breast cancers are found in women over age 55.
- Personal history of breast cancer: If a woman had breast cancer in one breast, there is an increased risk of developing breast cancer in another breast or in a different area of the previously affected breast.
- Family history: If a close female relative had breast cancer, there is an increased risk for developing it.
- Genes: Certain gene mutations that increase the risk of breast cancer can be passed from parents to children. The most well-known gene mutations are referred to as BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- Being obese increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Early menstruation: Having the first period before age 12 increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Late menopause: Women who do not start menopause until after age 55 are more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Having a first child at an older age: Women who don’t have their first child until after age 35 have an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Never being pregnant: Women who never became pregnant or never carried a pregnancy to full term are more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Hormone therapy: Women who take hormone therapy medications that combine estrogen and progesterone to treat the signs and symptoms of menopause have an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Drinking alcohol: Drinking alcohol increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Dense Breast Tissue: Women with more dense breasts are more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Radiation Exposure: Undergoing radiation treatment may increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
Tips to reduce the risk of Breast Cancer?
The following steps may help reduce the risk of breast cancer.

- Discuss with the doctor about breast cancer screening such as clinical breast exams and mammograms.
- Women may choose to become familiar with their breasts through breast self-exam for breast awareness.
- Limit alcohol intake to no more than one drink a day.
- Exercise most days of the week.
- Limit postmenopausal hormone therapy as it may increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Choose a healthy diet.
How is Breast Cancer diagnosed?
Several diagnostic tests and procedures including below help to confirm a diagnosis.
Physical examination of the breast: The doctor will check the breasts for lumps and other symptoms.
Mammogram: A type of X-ray that helps the doctor to detect any lumps or abnormalities in the breast.
Ultrasound: Helps the doctor to differentiate between a solid mass and a fluid-filled cyst.
MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) combines different images of the breast to help a doctor identify cancer or other abnormalities.
FNAC (fine needle aspiration cytology): A fine-gauge needle is used to remove fluid from the breast tissue for microscopic evaluation.
Biopsy: A sample of tissue is extracted and analyzed in a laboratory to indicate the type of cancer, stage of cancer, size of the tumor, invasive or non-invasive.
What are the treatment options?
Treatment depends on several factors and may include:
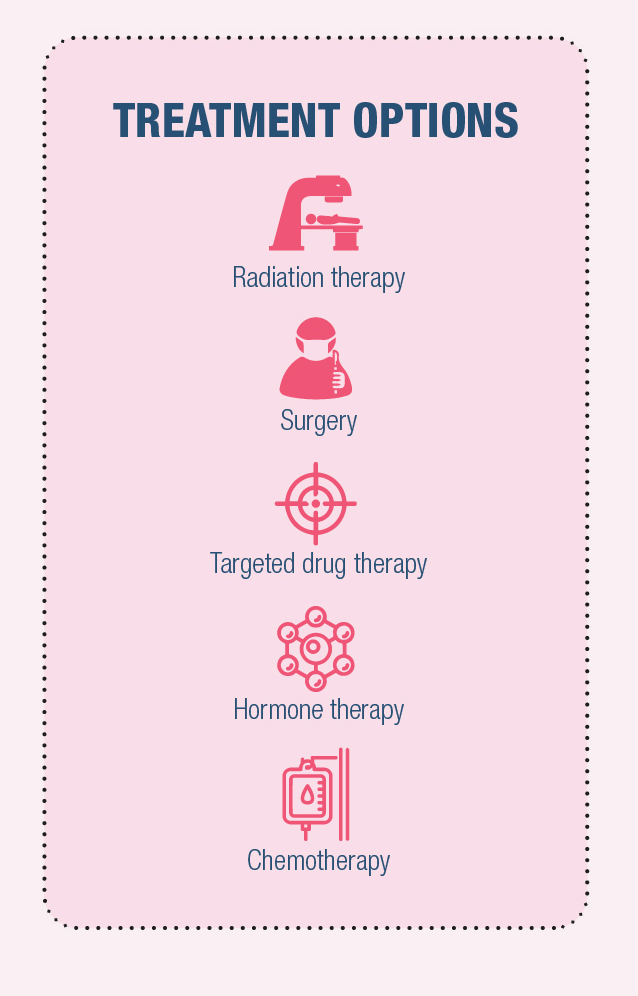
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery
- Targeted drug therapy
- Hormone therapy
- Chemotherapy
ABOUT US
Fit & Healthy Generation Kenya .
Reducing Non Communicable Disease burden through provision of equitable, diversified , all inclusive wellness & health programs
ALL CONTACTS
- Hurlingham Plaza, Argwings Kodhek
- +254 706 674 766
- info@fhgkenya.org
- Open 8 am - 5 pm Sunday closed
SUBSCRIBE
Sign up today for news updates


Leave a Reply